Crucial Ballistix Smart Tracer 1600MHz DDR3 4GB Kit Review
Andy Ruffell / 14 years ago
Results
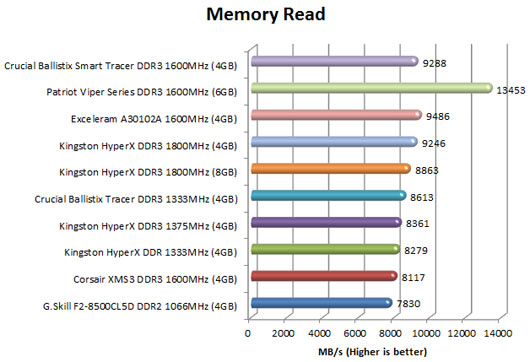
[COLOR=#000000]Memory Read
This benchmark measures the maximum achievable memory read bandwidth. The code behind this benchmark method is written in Assembly and it is extremely optimized for every popular AMD and Intel processor core variants by utilizing the appropriate x86, MMX, 3DNow!, SSE, SSE2 or SSE4.1 instruction set extension. The benchmark reads a 16 MB sized, 1 MB aligned data buffer from system memory into the CPU. Memory is read in forward direction, continuously without breaks.
In order to avoid concurrent threads competing over system memory bandwidth, Memory Read benchmark utilizes only one processor core and one thread.
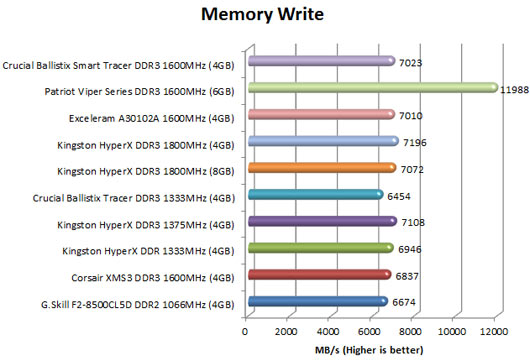
[COLOR=#000000]Memory Write
This benchmark measures the maximum achievable memory write bandwidth. The code behind this benchmark method is written in Assembly and it is extremely optimized for every popular AMD and Intel processor core variants by utilizing the appropriate x86, MMX, 3DNow!, SSE or SSE2 instruction set extension. The benchmark writes a 16 MB sized, 1 MB aligned data buffer from the CPU into the system memory. Memory is written in forward direction, continuously without breaks.
In order to avoid concurrent threads competing over system memory bandwidth, Memory Write benchmark utilizes only one processor core and one thread.
[/COLOR]
[COLOR=#000000]Memory Copy
This benchmark measures the maximum achievable memory copy speed. The code behind this benchmark method is written in Assembly and it is extremely optimized for every popular AMD and Intel processor core variants by utilizing the appropriate x86, MMX, 3DNow!, SSE, SSE2 or SSE4.1 instruction set extension. The benchmark copies a 8 MB sized, 1 MB aligned data buffer into another 8 MB sized, 1 MB aligned data buffer through the CPU. Memory is copied in forward direction, continuously without breaks.
In order to avoid concurrent threads competing over system memory bandwidth, Memory Copy benchmark utilizes only one processor core and one thread.
[/COLOR]
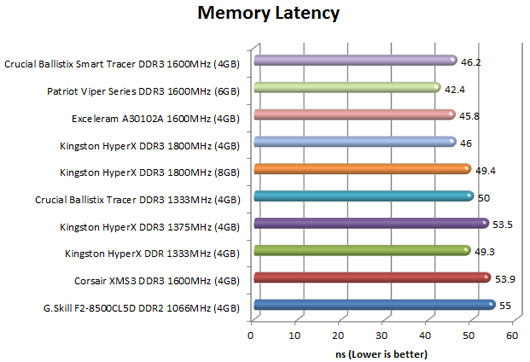
[COLOR=#000000]Memory Latency
This benchmark measures the typical delay when the CPU reads data from system memory. Memory latency time means the penalty measured from the issuing of the read command until the data arrives to the integer registers of the CPU. The code behind this benchmark method is written in Assembly, and uses 1 MB alignment, 1024-byte stride size. Memory is accessed in forward direction.
Memory Latency benchmark test uses only the basic x86 instructions and utilizes only one processor core and one thread.[/COLOR]