EVGA Supernova 750 G+ Gold Power Supply Review
Mike Sanders / 6 years ago
Test Procedure
At eTeknix we take the power supply testing procedure very seriously and have invested a lot of resources into acquiring the appropriate testing equipment. For all power supply reviews, we test the power supplies with dedicated power supply testing equipment. This means we are able to get the most accurate results from our testing as opposed to using software benchmarks (such as OCCT) or multi-meter readouts which are broadly inaccurate.

Testing Hardware
- Sunmoon SM-5500ATE Active Load Tester (1200W rated)
- Stingray DS1M12 USB Oscilloscope
- Voltcraft DT-10L laser tachometer
What the eTeknix Test Procedure Involves
- Testing each power supply at 20/40/60/80/100% load (with load balanced across all rails) and measuring PFC (power factor correction), efficiency (actual power divided by power “pulled at the wall”) and voltage regulation (deviance from expected voltages of 3.3/5/12 on the main rails).
- Measuring ripple with an oscilloscope at 20/40/60/80/100% load.
- Measuring fan speed after a stabilisation period of five minutes at each load scenario using the Voltcraft DT-10L laser tachometer and a reflective strip on the fan.
- Testing each power supply’s OPP (Over Power Protection) mechanism and seeing how many watts each power supply can deliver before shutting down
Other Things to Consider
- We recognise that a single 12-volt cable can provide only 6 Amps before overheating (which corrupts voltage regulation and efficiency) and so we used an adequate number of cables for each power supply to ensure there is not efficiency loss from poor cables selection
- Our Sunmoon SM-5500ATE power supply tester is not capable of testing more than 300W on each of the 12-volt rails so where a power supply provides more than 300W on a 12-volt rail that power is distributed over multiple 12-volt rails on the load tester. For example a power supply with one 12 volt rail supplying 750 watts would be spread equally over three 12 volt rails on the load tester, a power supply with two 450W 12v rails would be spread over four 12v rails on the load tester, two 225W 12v rails for each of the 12v rails on the unit.
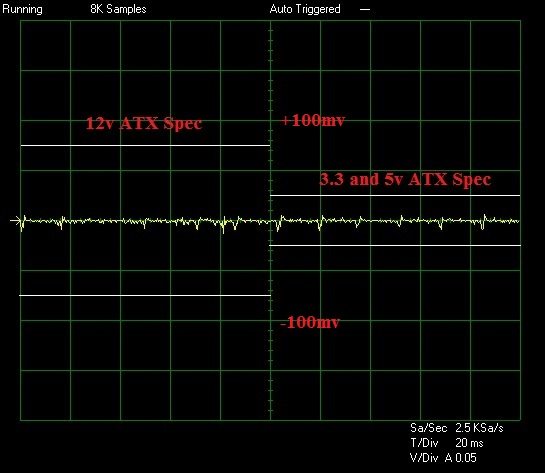
- We use the same time scale and horizontal millivolt scale on our oscilloscope for all ripple tests, that is a 20ms T/DIV (horizontal) and a 0.02 V/DIV (vertical) meaning the scale is from -80mV to +80mV, ATX spec dictates that the 12v rail must fall within 150mv of ripple and the 3.3/5 within 50mv so that scale allows us to include both 150 and 50mV peaks. (Some older PSU reviews use different scales which were later ditched as the visual representation they give is inadequate, in these reviews written measurements are provided only).
- Deviance is the terminology used to represent the way voltages diverge from the expected values
Voltage Regulation
To test voltage regulation we load the power supply to five different load scenarios that give an equal spread of load across every single rail. So that means 20% on all rails, 40% on all rails and so on. We then calculate the average deviance of each rail from its expected voltage. Ideally, anything of +/- 2% regulation is seen as a very good result.
Power Efficiency
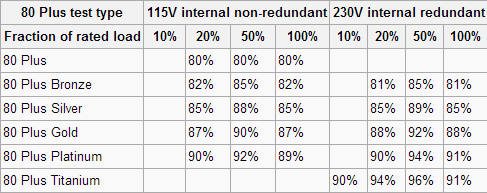
Power efficiency is measured by calculating actual supplied wattage divided by the wattage drawn at the wall/plug, multiplied by 100 to give a percentage. We then compare that to the particular 80 Plus certification the company claims to see if it meets that. You can see the 80 Plus certifications below, we always test power supplies at 230v.
Power Factor Correction
Power Factor Correction is the ratio of the real power flowing to the load, to the apparent power in the circuit. The aim of PFC is to make the load circuitry that is power factor corrected appear purely resistive (apparent power equal to real power). In this case, the voltage and current are in phase and the reactive power consumption is zero. The closer the number to one the better as this allows the most efficient delivery of electrical power (Source – Wikipedia).
Ripple
Noise and Ripple can easily be measured by an oscilloscope. These show how much voltage fluctuation there is on a particular rail. We tested the rail stability of the 3.3-volt, 5-volt and 12-volt rails using an identical time and millivolt scale for all graphs. millivolt ripple is measured by the peak to peak size of the voltage curve.
The latest ATX 12 volt version 2.3 specifications state that ripple from peak to peak must be no higher than 50 millivolts for the 3.3-volt and 5-volt rails, while the 12-volt rail is allowed up to 120 millivolts peak to peak to stay within specifications. Millivolt figures are stated to the closest increment of 5 given their variability.
OPP
Power supplies often quote as having various protection mechanisms such and the most important of these is Over Power Protection. In our testing we crank up the power draw until the power supply either shuts down (meaning the OPP mechanism is present and working) or blows up (meaning it is either not present or not working). We then note the maximum power consumption before the power supply shut down, or before it blew up.
Fan Speed
When testing in a power supply laboratory it is difficult to take fan noise readings as the noise from the Sunmoon test equipment and air conditioning corrupts everything. The next best thing in our circumstances was reading off the fan speed with a tachometer to get an idea for the noise. The ambient temperature during testing held constant at 22 degrees, with 1 degree of variation. Each power supply had a consistent time period of 5 minutes to stabilise between each load scenario.
In my experience, the following general relationships apply between noise levels and fan speeds, though it can vary greatly between the type of fan used.
- Below 800 RPM – Inaudible/Silent
- 800 to 1000 RPM – Barely audible
- 1000 – 1200 RPM – Audible but still quiet
- 1200 – 1400 RPM – Moderately noisy
- 1400 – 1800 RPM – Noisy
- 1800 RPM or above – Intolerable



















